Braimstorm
Kids already know...
" Living things are things which are alive.
Living things need air, food and water to live.
They also need Sun and light.
Living things are born. Living things die.
A rabbit a living thing, a tree is a living thing, we are a living things.
Living things are animals, persons and plants.
Living things live on Earth. There are also non-living things.
Non-living things don´t need air, food or water. They don´t move.
A table, a pencil, a car is a non-living thing. A river is a non-living thing, a mountain, a rock. There are natural non-living things and other that people make."
LIVING THINGS:
We come across living and non-living things daily. Most times it´s easy to diffentiate between living and nonliving things. Living things are active and alive. All living things are born, they need food and water, they need air, sunlight and they die. Some examples of living things arund us are plants, animals and human beings. Non living things do not grow, do not move, and they do not reproduce. Some of the examples of non-living things are a table, a chair, a bike, a river, a mountain, the sea.... There are natural non-living things and also manmade non-living things.LIFE PROCESSES:
There are 7 things that all living organism do - these are called "Life Processes." An organism is only alive if it does all seven life processes.
These seven processes are movement, respiration or breath, interaction or sensitivity, growth and change, reproduction, excretion and nutrition. ( Children in UK rememeber MRS NERG, the letter in this name stand for the life processes , you can play here with her. MRS NERG GAME)
Nutrition: All living things get nutrients froom food to grow and survive.
Interaction or sensitivity: All things react to their enviroment.
Reproduction: All living things reproduce to make more living things of the same type.
Biologist
today have classified and divided all living things into five groups
they call Kingdoms. These kingdoms are based on how living things are
the same and how they are different. It is important that you understand
that biologists are still learning about our world, and are making new
discoveries every single day. As our knowledge about the world around us
improves, scientists might find a better way to organize and classify
life. As a result, these five kingdoms may someday change. The five kingdoms currently accepted by most (but not all) scientists are
the Monera Kingdom, the Protist Kingdom, the Fungi Kingdom, the Plant
Kingdom, and the Animal Kingdom.
 |
| FUNGI KINGDOM |
 |
| MONERA KINGDOM |
| PROTIST KINGDOM |
 |
| ANIMAL KINGDOM |
 | |||||||||||
| ANIMAL KINGDOM |
/tbody>
 | ||||||||||||
| PLANT KINGDOM |
ANIMALS.
Animlas are living things. Lions and rabbits are a animals. Inscts,birds, fish and reptiles are animasl too. Also human beings.
Nutrition
All animals eat otger living things. Different animals eat different living things.
Panda bears eat bamboo. Bees eat nectar. Pigs eat worms, roots and nuts. Sharks eat other fish.
Interaction.
Animals react to enviroment to survive. Animals move around to find their food, to scape from other animals. Different animals move in different ways.
Fish swim. Sparrows fly,cheetahs run, snakes slither and some other climb.
Animals can´t talk, but they make sounds to communicate with other animals. Some animals live together in groups.
Reproduction:
Animals produce babies. Some animals are born from eggs. Other animals are born directly from their mothers.
A puppy is born directly from her mother.
A duckling is born from eggs.
Interaction
FINDING OUT AT HOME...
HOW DO ANTS COMMUNICATE???
Kids discovered at home that....
PLANTS
Trees, bushes and grasses are all plants. Flowers, leaves, roots and fruit are parts of a plant.
Nutrition.
Plants make their own food. They use the sunlight, air, water and nutrients from soil to make their food.
Reproduction:
Plants can make new plants. Many plants make seeds. Seeds grow into new plants.Other plants grow into new plants. Other plants grow a new plant from their plants.
Plants can´t go from one place to another but they do move their parts.The roots of a plant grow toward s water. Some flowers turn to face the Sun.
Nutrition.
We eat food from other animals, fish, meat, milk and eggs. We also eat fruit, vegetables, pulses and cereals.
We prepare our food and have diferent meals along the day.
Inteaction.
Humans can move arund, we can walk, run, jump... We have also invented machines which allow us to fly. We communicate in many different ways, by talking, touching and writing. We also intearct with our enviroment.
Reproduction.
Human babies are born directly from their mothers. Before that, the baby grows inside their mothers for nine months.Humans take many years to become independent.
ANIMALS
How can we classify veretebrates?
Fish: Fish are oviparous. They are born from eggs. They have scales. They live in water.
Reptiles: Reptiles are oviparous. They have scales. Some live in water, but most live on land.
Mammals:
Mammals are viviparous. Theeir babies grow inside the mother and are born alive. Most have hair. Some live in water, but most live o land. Some can fly.
Animals are living things. Animals are classified in different groups.
All animals are divededinto two big groups:Vertebrate animals and invertebrate animals.
What is a vertebrate?
Vertebrate animals are those which have a skeleton inside them. An important part of their skeleton is the backbone. Most vertebrate have a head, a trunk, limbs, and a tail.
Some vertebrates, like frogs, don´t have a tail and others, like snakes, don´t have limbs.
Fish: Fish are oviparous. They are born from eggs. They have scales. They live in water.
Reptiles: Reptiles are oviparous. They have scales. Some live in water, but most live on land.
Birds: Birds are oviparous. They have feathers. Most birds can fly.
Mammals:
Mammals are viviparous. Theeir babies grow inside the mother and are born alive. Most have hair. Some live in water, but most live o land. Some can fly.
What is an invertebrate?
Invertebrate don´t have a backbone. They are usually smaller than vertebrate. All invweretebrate are oviparous. Most animals on the Earth are invertebrate. Some are land animals and some are water animals.
Molluscs.
Molluscs have a soft, muscular body. Some, like snails, have a shell. Many molluscs live in the sea. Mussels, oysters and octopuses are all mollucs.
Arthropods.
Arthropods are the biggest group of invertebrate. Their bodies are divided into 3 parts. They have a hard skin and joints in their legs. Insects, (ants and bees) and arachnids
(spiders and scorpions) are arthropods.
Worms. Worms have a long soft body.They don´t have shells. Some live on land and others live in water. Some worms are parasites. They live in other animal and feed on them.
Sponges. Sponges have soft bodies covered with little holes. They live in water.
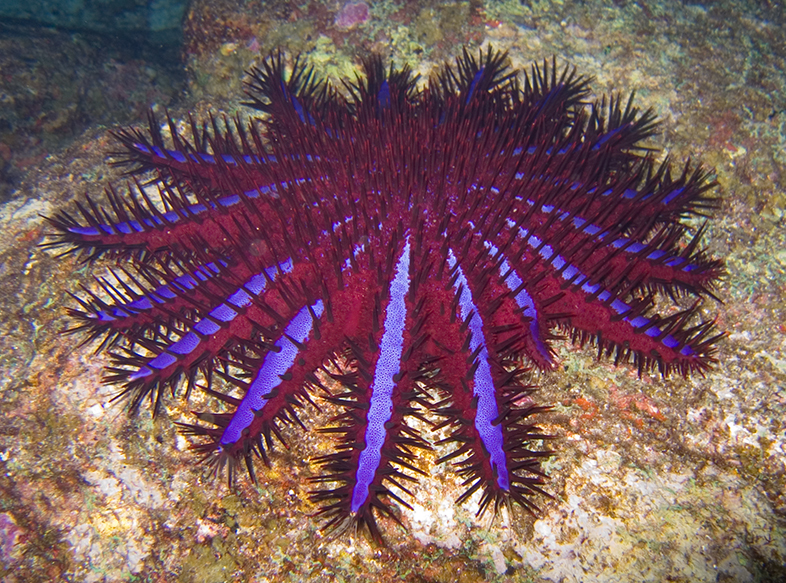
Starfish. Starfish are protected by hard outer parts. They live in water. They usually have 5 arms, but they can have even 20!
PLANTS
Plants are living things. They need air, sunlight and minerals they get from water and soil.
They make their own food. They form seeds to reproduce. They can´t move from one place to the other, bur they react to the environment.
PARTS OF A PLANT
The Roots anchor the plant to the ground.
The Stem connects the roots with the leaves.
The Leaves make food for the plant by using sunlight, air and water.
The Flowers contain the reproductive organs of the plant.
Plants are living things. They need air, sunlight and minerals they get from water and soil.
They make their own food. They form seeds to reproduce. They can´t move from one place to the other, bur they react to the environment.
PARTS OF A PLANT
The Roots anchor the plant to the ground.
The Stem connects the roots with the leaves.
The Leaves make food for the plant by using sunlight, air and water.
The Flowers contain the reproductive organs of the plant.
Roots, stems, and leaves of plants vary depending on the type of plant and its environment.
Roots can be thick and hairy. Onions plants have Hairy roots, tress have thick roots. Sometimes people eat roots, for example, the roots.
Some plants have woody stems, they are hard and rigid. Some of them are trees, these stems are called trunks.
 |
| WINNER-MILLER-TREE |
Bushes are plants with more than one stem coming from the ground. Some of them are of moderate lenght, but some are really tall. Very often, their stem is woody and rigid.
Green Stems are soft and flexible, for example, the stem of wheat.
Leaves can be different shape. Their edge can be smooth, toothed or lobed. There are also compound an simple leaves, depending on the numbers of blades they have connected directly to the petiole.
OUR SCHOOL VEGETABLE GARDEN.
Last Friday, 20th February we visited the school vegetable garden. There are many plants there. There are tress, bushes and green plants. Some of the green plants are vegetebles. The beanstalks are already blossoming (flowers coming out).
We were looking at the trees, some of them are completely covered with leaves even if we are in winter. They are evergreen trees, and they make leaves all year. There are also decidious trees, these trees lose all their leaves in Autumn and get new ones in spring. We walked around and collected some leaves and classified them, compound and simple leaves, round-shaped, heart-shaped... One of the trees, have some fruits, we think they are oranges, but they might be tangerins...
We were lucky it was suuny and we really enjoyed this activity....
Mireia has brought a gorgeous almond tree, it´s got some sprouts, and we are going to plant it in the vegetable garden.
HOW DO PLANTS REPRODUCE?
The flowers contain the male and female reproductive organsm corolla and calyx. Seeds form inside the flower. The fruit forms around the seeds.
The corolla is formed by petals. It si colorful to attract insects. It protects the reproductive organs.
The stamen is the male reproductive organ. The anther contains pollen grains. The filament holds the anther up.
The calyx is formed by sepals. It protects the rest of the flowers.
The carpel is the female reproductive organ. The stigma is sticky to catch pollen. The ovary contains ovules.
A pollen grain and an ovule join to make a seed. The ovary develops into a fruit.
WHAT ARE PLANTS USED FOR?
Since ancient times peole have always the plants. We have eaten plantsFruits, herbs, roots, leaves...We also use it to make paper, medicines, pefumes, for buildings...
We use cotton thread from the flowers to make clothes.
We get wood from the trunks and branches of trees. We use it to make furniture, buildings...
We get cork from some trees.
We also get resine to make ink, rubbers and even chewing gum!!!
LLLLLL LLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL
EXPERIMENTS
HUMAN BODY
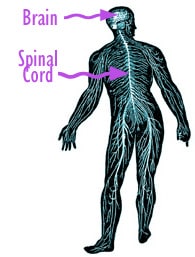
We are able to relate to what is around us through our Senses. This means we can recognise and respond to changes.The Nervous System receives information from the sense organs and chose the best response .
The nervous system controls everything that happens in our bodies. It is made up of brain, spinal cors and the nerves.
FIVE SENSES
We have five senses: Sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch.
SIGHT
The eyes are the organs of Sight. We use our eyes to identify colour, shape, size and sistance.
The eye has different parts: The iris, the pupil, the lens, the retina and the optic nerve.
HEARING
The ears are the organs of hearing. We use our ears to heaqr sounds. The ear has 3 parts: The outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
SENSE OF TASTE AND SMELL.
The tongue is the organ of taste. Its upper surface is covered in taste buds. The human nose is also an organ of taste as well as smell.The so-called taste-buds on our tongues can only distinguish four qualities – sweet, sour, bitter and salt -all other ‘tastes’ are detected by the olfactory receptors high up in our nasal passages.
SENSE OF TOUCH
Our sebse of touch allows us to receive information about the environment. The skin is the organ of touch and it´s all around our body.
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
All animals need to eat food to get energy to live. But in order nto use this food, they have to break it down in a process called digestion. And so all animals have a group of connected organs called the Digestive System.
In humans the process of digestion begins in the mouth where the food is chewed into small piecesby the teeth. The tongue helps by moving these pieces around. These pieces are covered by saliva. The saliva makes the food slippery so that it is easier to swallow.
Once the food is swallowed, it passes through pharynx the which is like a gate that sends food into the esophagus, which is like a a gate that sends food into the stomach. Once in the stomach, the food is mixed with liquids and crushed some more.
After spending some time in the stomach, the food is sent into the small intestine where nutrients are absorved. The liver helps by producing some digestive juices called bile.
Next the remainding food goes to the large intestine and it is pushed into the rectum where it waits before leaving the body.
EXCRETORY SYSTEM
Our excretory system helps our bodies to get rid of excess water and waste products.


















No comments:
Post a Comment